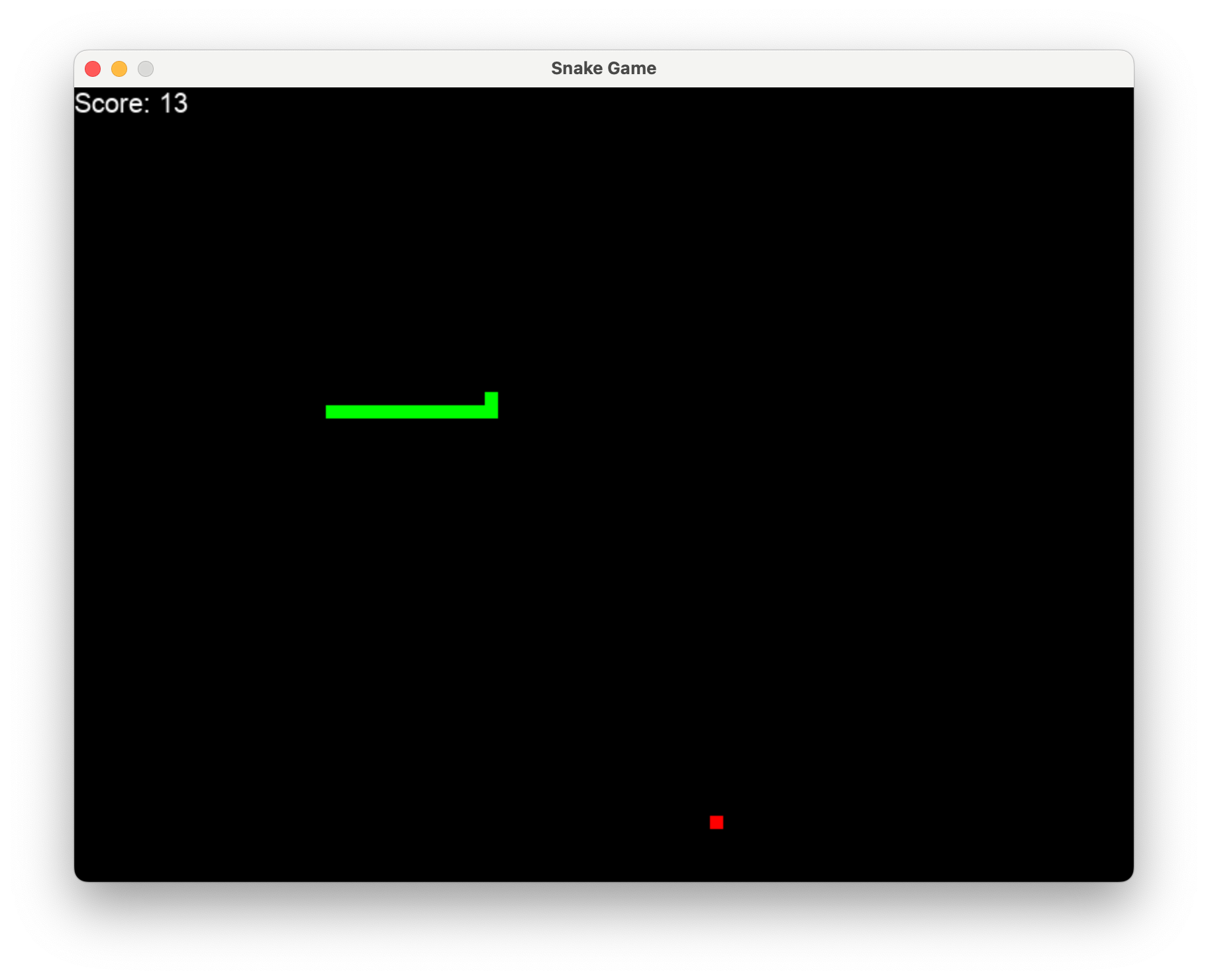
Codebase Generator
The LLM Automatic Computer Framework (L2MAC) is state-of-the-art for generating large complex codebases with a Large Language Model.
The following provides a complete example of creating an simple codebase. Run:
from l2mac import generate_codebase
# run pip install pygame==2.1.2
codebase: dict = generate_codebase(
"Create a beautiful, playable and simple snake game with pygame. Make the snake and food be aligned to the same 10-pixel grid.",
steps=2,
)
print(codebase) # it will print the codebase (repo) complete with all the files as a dictionaryThis will create a new workspace folder in your local directory where you run this script, including all the files generated while running and when L2MAC has completed. The final output codebase will be within the newly generated folder in the local workspace directory, organized by the time and date as the sub-folder name.
The output should look something like this.
snake_game
├── main.py
├── requirements.txt
└── test_main.pyThe complete raw output generated by the above is given below.
main.py
import random
import sys
import pygame
# Initialize Pygame
pygame.init()
# Screen dimensions
SCREEN_WIDTH = 800
SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600
# Colors
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
# Set up the display
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT))
pygame.display.set_caption("Snake Game")
# Frame rate
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
FPS = 10
# Grid size
GRID_SIZE = 10
# Snake class
class Snake:
def __init__(self):
self.length = 1
self.positions = [((SCREEN_WIDTH // 2), (SCREEN_HEIGHT // 2))]
self.direction = random.choice(["up", "down", "left", "right"])
self.color = GREEN
self.score = 0
self.speed = 10
def move(self):
cur_x, cur_y = self.positions[0]
if self.direction == "up":
new_head = (cur_x, cur_y - GRID_SIZE)
elif self.direction == "down":
new_head = (cur_x, cur_y + GRID_SIZE)
elif self.direction == "left":
new_head = (cur_x - GRID_SIZE, cur_y)
elif self.direction == "right":
new_head = (cur_x + GRID_SIZE, cur_y)
self.positions.insert(0, new_head)
if len(self.positions) > self.length:
self.positions.pop()
def grow(self):
self.length += 1
self.score += 1
self.speed += 1
global FPS
FPS = min(60, self.speed) # Cap the FPS at 60 to prevent it from getting too fast.
# Food class
class Food:
def __init__(self):
self.position = (0, 0)
self.color = RED
self.randomize_position()
def randomize_position(self):
self.position = (
random.randint(0, (SCREEN_WIDTH // GRID_SIZE) - 1) * GRID_SIZE,
random.randint(0, (SCREEN_HEIGHT // GRID_SIZE) - 1) * GRID_SIZE,
)
# Main game loop
def main():
# Game initialization
snake = Snake()
food = Food()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
if event.key == pygame.K_UP and snake.direction != "down":
snake.direction = "up"
elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN and snake.direction != "up":
snake.direction = "down"
elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT and snake.direction != "right":
snake.direction = "left"
elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT and snake.direction != "left":
snake.direction = "right"
# Game logic
snake.move()
if snake.positions[0] == food.position:
snake.grow()
food.randomize_position()
# Check for collisions
if snake.positions[0] in snake.positions[1:]:
# Game over logic
print("Game Over! Your score was:", snake.score)
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
# Render the game state
screen.fill(BLACK)
for pos in snake.positions:
pygame.draw.rect(screen, snake.color, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE))
pygame.draw.rect(screen, food.color, pygame.Rect(food.position[0], food.position[1], GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE))
# Display the score
font = pygame.font.SysFont("arial", 20)
score_text = font.render("Score: " + str(snake.score), True, WHITE)
screen.blit(score_text, [0, 0])
pygame.display.update()
clock.tick(FPS)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()test_main.py
import pygame
import pytest
from main import Food, Snake
# Mock pygame to run headless
pygame.display.set_mode = lambda x: None
pygame.init = lambda: None
pygame.quit = lambda: None
@pytest.fixture
def snake():
return Snake()
@pytest.fixture
def food():
return Food()
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"direction, expected_position",
[("up", (400, 290)), ("down", (400, 310)), ("left", (390, 300)), ("right", (410, 300))],
)
def test_snake_movement(snake, direction, expected_position):
snake.direction = direction
snake.move()
assert snake.positions[0] == expected_position
@pytest.mark.parametrize("initial_score, expected_score", [(0, 1), (5, 6)])
def test_snake_eating(snake, food, initial_score, expected_score):
snake.score = initial_score
snake.positions[0] = food.position # Simulate snake eating the food
snake.grow()
assert snake.score == expected_score
@pytest.mark.parametrize("initial_length, expected_length", [(1, 2), (3, 4)])
def test_snake_growing(snake, initial_length, expected_length):
snake.length = initial_length
snake.grow()
assert snake.length == expected_lengthrequirements.txt
pygame==2.1.2
pytestPlayable Snake Game
Click here for the complete files on github or download them here. The code and prompt to generate this is here.